异常
1732字约6分钟
2025-09-23
有时候出现了一个不算致命的问题,就导致程序崩溃,这样程序的健壮性就不是很好,所以Java设计者就提供了一个异常处理机制来解决这个问题

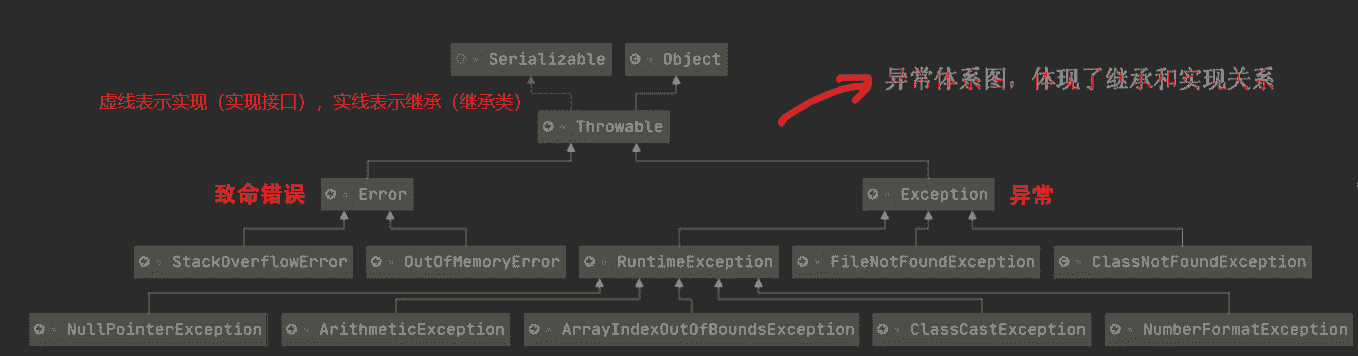
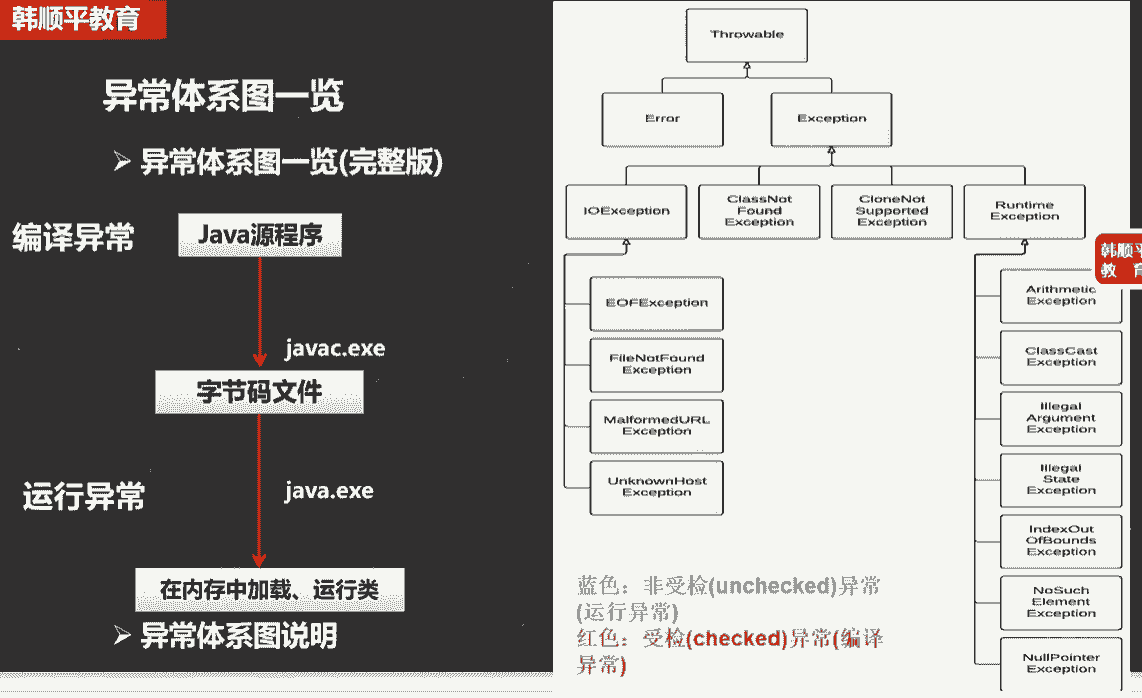
编译异常就是在编译时的异常,运行异常就是在运行时的异常

try-catch-finally
try里面是用来运行可能会异常报错的代码catch可以有多个,用来捕获不同的异常(进行不同的业务逻辑处理),但是父类异常要写在子类异常的后面,如果发生异常只会匹配一个catchfinally中的代码不管有没有异常都会被执行
public class Demo01 {
// throws Exception是默认不用写就有的
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
try {
String name = "zhangsan";
int x = Integer.parseInt(name); // 数字格式不正确异常
// 后面的代码将不在执行
int c = a / b; // 数字运算异常
System.out.println(c);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) { // 子类异常
// 输出类型转换异常信息
// 发生异常只会匹配一个 catch
// 所以该 catch 被执行
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (ArithmeticException e) { // 子类异常
// 输出数字运算异常信息
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) { // 父类异常要写在子类异常后面
// 输出异常信息
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
System.out.println("finally代码块已被执行");
}
System.out.println("程序继续运行。。。");
}
}// 运行结果
For input string: "zhangsan"
finally代码块已被执行
程序继续运行。。。try-finally
原理和 try-catch-finally 差不多
使用场景:程序要报错时,执行finally代码(比如通知之类的代码)
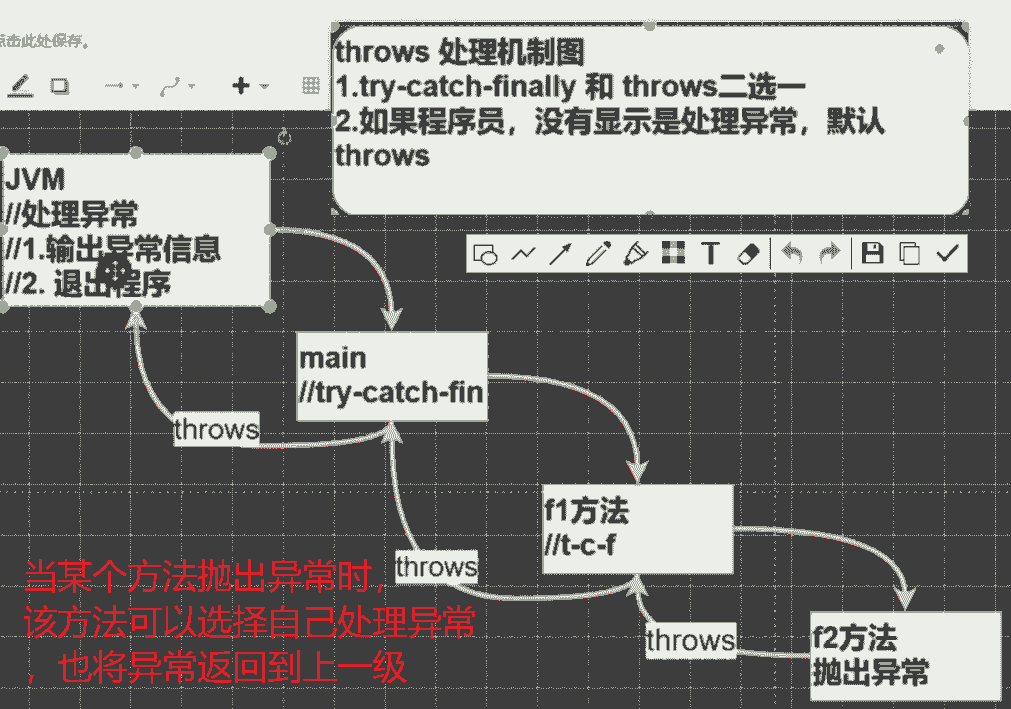
throws
throws 关键字用于在方法声明中指定该方法可能抛出的异常。
简述:该代码的作用是谁调用,谁处理
运行原理:当方法内部抛出指定类型的异常时,该异常会被传递给调用该方法的代码,并在该代码中处理异常,当然该代码也可以继续往上传,当异常传到JVM的时候直接输出异常信息并退出程序
/* 创建文件流
当方法可能会出现某个异常的时候就可以使用throws来指定异常类型
* 1.如果要处理的异常太多了就用Exception
* 2.throws后面的异常类型可以是子类也可以是父类(Exception)
* 3.throws后面也可以是异常类型列表,就是throws后面可以接多个异常类型
* */
public static void f2() throws FileNotFoundException,NullPointerException {}
public static void f3() { f4(); } // f4() 抛出编译异常,所以会报错
public static void f4() throws FileNotFoundException {}
public static void f5() { f6(); } // f6() 抛出运行异常,所以不会报错
public static void f6() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBounds {}异常细节
对于编译类型,程序中必须处理,
try-catch-finally和throws二选一对于运行时异常,程序中如果没有处理,则默认使用
throws的方式处理子类重写父类的方法时,对抛出异常的规定:子类所抛出的异常类型要么和父类的异常一致,要么就是父类的异常的子异常
class A1 { public void info() throws RuntimeException {} } class B1 extends A1 { @Override public void info() throws NullPointerException {} }在
throws的过程中,如果有方法已经try-catch了,则就没有必要在写throws了/* * 因为f2抛出了编译异常,但是f2方法有没有处理异常,所以就将异常返回给调用方法 * 所以调用方法f1如果不处理异常或者抛出异常则会报错 * 如果f2抛出的是运行时异常,那么调用方法则可以不用处理异常,因为在Java中对于运行时异常则有默认处理机制 * */ public void f1() throws FileNotFoundException { // 两种方法二选一 // 处理异常 // try { // f2(); // } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // e.printStackTrace(); // } // 抛出异常 f2(); } public static void f2() throws FileNotFoundException {}在异常中如果有
catch则先运行catch中的代码,然后在运行finally中的代码;如果没有
catch则先运行finally中的代码,然后在抛出异常// 例子一 try { // 下面抛出异常,但异常会被catch捕获,所以会先执行catch中的代码 // 之后在执行finally中的代码 throw new RuntimeException("异常"); } catch (RuntimeException e) { // 输出运行时异常信息 System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } finally { System.out.println("finally代码块已被执行"); } // 例子二 try { // 下面抛出异常,在抛出异常之前会优先执行finally中的代码 throw new RuntimeException("异常"); } finally { System.out.println("finally代码块已被执行"); }
自定义异常
- 自定义:自定义异常类名(就是自己写的)继承
Exception和RuntimeException - 继承
Exception则属于编译异常 - 继承
RuntimeException则属于运行异常(一般使用运行异常)
public class Custom {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int age = 190;
if (!(age >= 18 && age <= 120)) {
// 抛出自定义异常对象
// 通过Age将异常信息传给异常
// 如果只是单纯的输出异常信息,其实下面的代码可以简写成 throw new RuntimeException("年龄不满足要求。。。");
throw new Age("年龄不满足要求。。。");
}
System.out.println("年龄正常。。。");
}
}
// 自定义异常
class Age extends RuntimeException {
public Age(String message) {
super(message);
}
} public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = null;
try {
st(name);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public static String st(String name) throws Exception {
if (name == null) {
throw new Exception("不能为空");
}
}
// 输出结果
不能为空throw和throws的区别
| 意义 | 位置 | 后面接的东西 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| throw | 手动生成异常对象的关键字(自定义异常) | 方法体中 | 异常对象 |
| throws | 异常处理的一种方式 | 方法声明中 | 异常类型 |
常见的运行时异常

空指针异常(NullPointer)
public class NullPointer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = null;
// name = null,所以没有长度
System.out.println(name.length());
}
}数字运算异常(Arithmetic)
public class Arithmetic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 分母不能为 0
System.out.println(10 / 0);
}
}数组下标越界异常(ArrayIndexOutOfBounds)
public class ArrayIndexOutOfBounds {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
// 循环数超出数组范围
for (int i = 0; i <= arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}类型转换异常(ClassCast)
public class ClassCast {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A b = new B();
B a = (B)b;
// C继承A,b是A,但是b指向的是B
// 所以A = B
// 因此C 不等于 B
C c = (C)b;
}
}
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C extends A {}数字格式不正确异常(NumberFormat)
public class NumberFormat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "string";
// 字符string无法转换为数字
int a = Integer.parseInt(s);
}
}常见的编译异常

